Managing Pap Smear Abnormalities
It is very stressful to find out pap smear abnormailities.
As part of further investigations, Dr Joshi performs “COLPOSCOPY” at her rooms, to find out any abnormal areas on the cervix.
Depending on the biopsy results after the Colposcopy, decision about further management can be discussed with the patient.
The Cervical Screening Test is a quick and simple procedure to check the health of your cervix.
The Cervical Screening Test replaces the two-yearly Pap test for people. If you’re aged 25 to 74 you should have your first Cervical Screening Test two years after your last Pap test.
The Cervical Screening Test will look and feel the same as the Pap test.
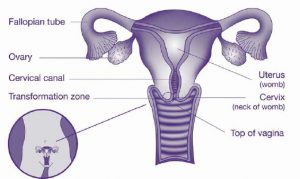
The Pap test looked for cell changes in the cervix, whereas the Cervical Screening Test looks for the human papillomavirus (known as HPV) which can lead to cell changes in the cervix (see diagram of the cervix below).
HPV is a common virus that can cause changes to cells in your cervix, which in rare cases can develop into cervical cancer.
Once you have had your first Cervical Screening Test, you will only need to have one every five years instead of every two, if your results are clear.
The test is a quick and simple procedure to check the health of your cervix. Your cervix is the opening of the uterus (neck of the womb), and is at the top of your vagina.
If you have ever had a Pap test before, the way your healthcare provider does the Cervical Screening Test will look and feel the same.
The procedure might be a bit uncomfortable, but it shouldn’t hurt.
If you are 25 to 74 years old and have had a Pap test, you should have your first Cervical Screening Test two years after your last Pap test.
If you have symptoms at any age, such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, pain or discharge, you should discuss these with your healthcare provider immediately.
Return to screen in five years
Your results show you do not have a HPV infection. The National Cervical Screening Program will send you a reminder to have your next Cervical Screening Test in five years.
Return to screen in 12 months
Your results show you do not need further investigation but you should have a repeat test in 12 months.
This is because you have a HPV infection. It is likely to be cleared by your body within the next 12 months.
The repeat test checks if the infection has gone and if so, you are safe to return to five yearly screening.
If the repeat test shows a HPV infection is still present, you may need further investigation from a specialist.
If you have a HPV infection, it does not mean you have cervical cancer. It takes about 10 to 15 years for cervical cancer to develop, and cervical cancer is a rare outcome.
Refer to a specialist
Your results show you have:
- A type of HPV infection that requires further investigation, or,
- Abnormal cells were found that require treatment
Your healthcare provider will refer you to a specialist for a follow-up test called a colposcopy test.
Unsatisfactory test result
An unsatisfactory test result means the laboratory cannot read your sample. This means you will need to come back for a repeat test in six weeks.
This result might happen if the number of cells collected is too small. An unsatisfactory result does not mean there is something wrong.
If your healthcare provider refers you to a specialist for a follow-up test, they will perform a colposcopy test.
A colposcopy is an examination of your cervix. During this examination, the specialist will use a device called a colposcope (which looks like a pair of binoculars on a stand) to get a magnified view of your cervix.
To have a colposcopy test, your specialist will ask you to lie on an examination bed with your legs supported, in a similar position to when you have a Cervical Screening Test. Like the Cervical Screening Test, the specialist will insert a speculum into your vagina. The specialist will then put a special liquid onto your cervix to highlight any abnormal cells.
The specialist will then look through the colposcope to carefully examine your cervix. The colposcope itself does not enter your body.
This examination usually takes 10 to 15 minutes and most people do not experience any pain. However, you may have some discomfort from having the speculum inside your vagina.
If areas of your cervix appear abnormal during a colposcopy test, the specialist may take a small sample of tissue to send to a laboratory for testing. This is a biopsy.
If you have a biopsy, you may have some pain for a short time.
It may take up to two weeks for the results of your biopsy to come back to your healthcare provider. When the results are back, you should make an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss the findings and talk about treatment, if needed.
If abnormal cells are found during your colposcopy, further treatment may be required.
Treatment options may include:
Wire loop excision
During this procedure, the abnormal cells are removed from your cervix with a wire loop. The procedure takes 15 to 30 minutes.
Laser
Laser treatment removes the abnormal cells using heat from a laser beam. The procedure takes 15 to 30 minutes.
Cone biopsy
In this minor operation, a cone-shaped section of the cervix which contains the abnormal cells is removed. A general anaesthetic is normally needed and a day or overnight hospital stay for recovery may also be required.
http://www.cancerscreening.gov.au/internet/screening/publishing.nsf/Content/about-the-new-test
http://www.papscreen.org.au/forwomen/aboutpaptests/thetesthttps://www.ranzcog.edu.au/RANZCOG_SITE/media/RANZCOG-MEDIA/Women%27s%20Health/Statement%20and%20guidelines/Clinical-Obstetrics/Cervical-cancer-screening-in-Australia-(C-Gyn-19)-Review-July-2017.pdf?ext=.pdf
https://www.ranzcog.edu.au/Statements-Guidelines
https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Abnormal-Cervical-Cancer-Screening-Test-Results

